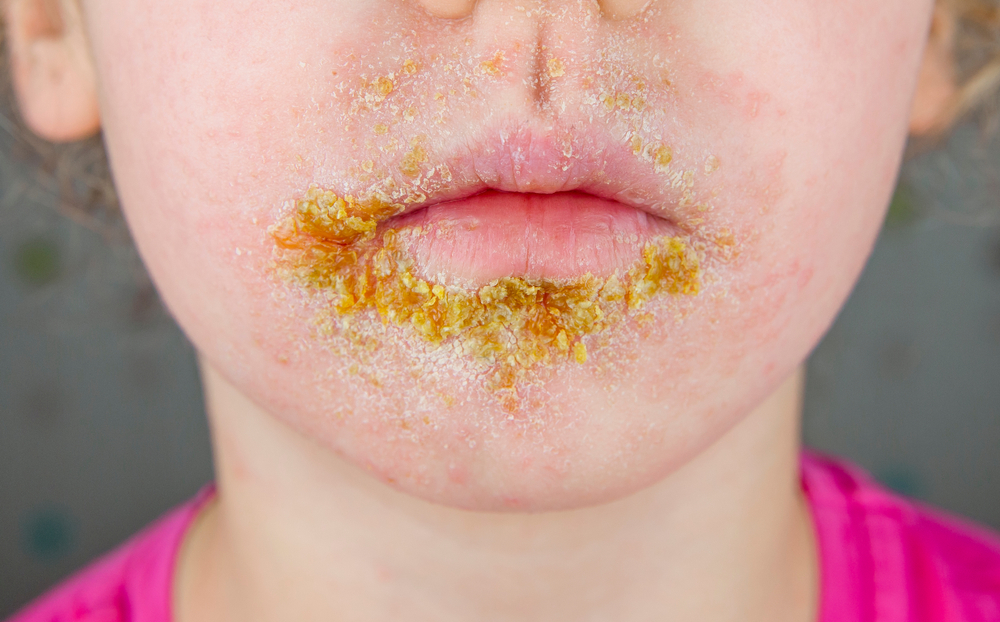
Impetigo is a highly contagious bacterial skin infection that causes red sores that quickly rupture, forming honey-coloured crusts.
Impetigo is usually not serious, but it can be uncomfortable and unsightly. It spreads easily through direct contact with an infected person or by touching contaminated objects.
Impetigo symptoms
You may have impetigo if you have any of the following symptoms:
- Small red spots or blisters on the skin
- Fluid-filled blisters that rupture easily, leaving behind moist, raw areas
- Thick, golden-yellow crusts that resemble dried honey or cornflakes
- Itchy and uncomfortable skin
- Swollen, tender lymph nodes
Impetigo causes
Impetigo is primarily caused by two types of bacteria: Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes. These bacteria can enter the skin through cuts, scrapes, insect bites, or other breaks in the skin’s barrier.
The following factors increase the risk of developing impetigo:
- Direct contact with an infected person
- Touching contaminated objects such as towels, clothing, or bedding
- Pre-existing skin conditions, such as eczema or dermatitis
For more information on the causes of impetigo, please visit our blog page.
Frequently asked questions about impetigo
What’s impetigo?
Impetigo is a contagious skin infection caused by bacteria, typically Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes. It results in red sores or blisters that ooze and form a yellowish crust.
Is impetigo contagious?
Yes, impetigo is highly contagious. It spreads through direct contact with an infected person or contaminated objects like towels or clothing.
What are the symptoms of impetigo?
Symptoms of impetigo include red sores, blisters, or lesions that burst and develop a yellowish-brown crust, itching, and swollen lymph nodes in severe cases.