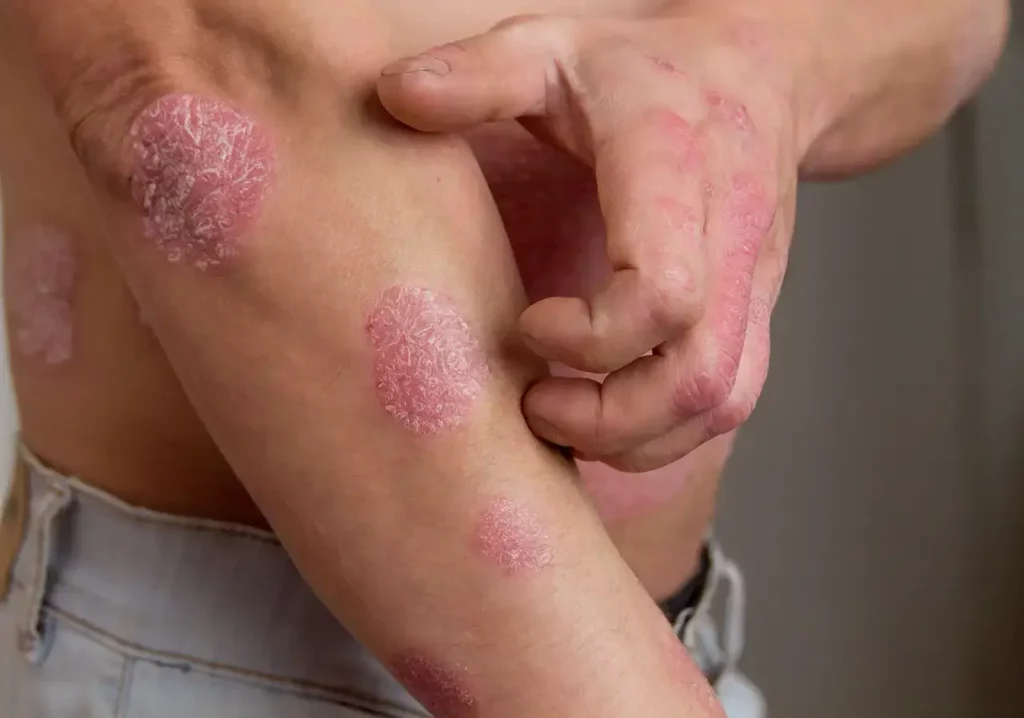
Psoriasis is a chronic skin condition where skin cells build up rapidly, causing thick, red patches with silvery scales. It affects around 2-3% of people globally.
Beyond its visible symptoms, like red, inflamed skin, psoriasis can lead to itching, discomfort, and even pain, making daily life challenging.
Seeking the best treatments for psoriasis isn’t just about improving your appearance, it’s about regaining control over your life. It’s about being able to engage fully in work, social activities, and relationships without the constant discomfort. In the next sections, we’ll explore effective treatments to help you manage your psoriasis and improve your well-being.
How to treat psoriasis
Managing psoriasis means finding the right mix of treatments for you. There’s a range of options, from creams to medications, each with its benefits and considerations.
In the next sections, we’ll break down these treatments, so whether you’re new to psoriasis or exploring alternatives, you can make informed choices for managing your condition effectively.
Topical creams and ointments
When it comes to managing psoriasis, topical creams and ointments are often the first line of defence. These treatments, applied directly to your skin, come in various forms and work by reducing inflammation, slowing skin cell growth, and relieving itching.
Corticosteroids are commonly prescribed for flare-ups, helping to reduce redness and itching. However, long-term use can lead to side effects like skin thinning.
Calcineurin inhibitors, such as tacrolimus and pimecrolimus, are also effective in calming inflammation, especially in sensitive areas like the face and genitals.
Other options include vitamin D analogues and retinoids, which help slow down skin cell growth and promote normal turnover.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy, also known as light therapy, is a treatment that exposes your skin to ultraviolet (UV) light under medical supervision. It can help slow skin cell growth and reduce inflammation.
There are a few types:
UVB Therapy
UVB Therapy is a common form of phototherapy that utilises a wavelength of light that is not visible to the human eye.
During each session, the patient is exposed to this UVB light for a few minutes. However, to achieve optimal results, patients may need to visit the hospital 2 or 3 times a week for a period of 6 to 8 weeks.
PUVA Therapy
Before you begin PUVA therapy (psoralen plus ultraviolet A), you’ll take a medication containing psoralens or apply directly to your skin to make it sensitive to light. Then, your skin is exposed to UVA light.
This treatment is usually for severe psoriasis not responding to other treatments. Side effects may include nausea, headaches, and skin irritation. You might also need to wear special glasses after the treatment to prevent cataracts from developing.
However, long-term use isn’t recommended due to an increased risk of skin cancer.
Systemic oral and injected medications
When topical treatments and phototherapy aren’t providing sufficient relief, systemic medications may be considered. These medications work from within the body to target the underlying causes of psoriasis and modulate the immune system’s response.
Oral Medications
Oral medications for psoriasis include retinoids, methotrexate, and cyclosporine.
Retinoids, such as acitretin, help to slow down skin cell growth and reduce inflammation. Methotrexate and cyclosporine work by suppressing the immune system, thereby alleviating symptoms of psoriasis.
However, these medications may have significant side effects and require close monitoring by a healthcare provider.
Biologic Drugs
Biologic drugs are a newer class of medications that target specific molecules involved in the immune response, such as tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) or interleukins.
These drugs are administered via injection or infusion and are highly effective for many people with moderate to severe psoriasis.
Examples of biologics used to treat psoriasis include adalimumab, etanercept, ustekinumab, and secukinumab.
Frequently asked questions about treating psoriasis
What are the side effects of psoriasis medications?
Side effects of psoriasis medications may include nausea, headaches, and increased risk of infections. It’s essential to discuss risks with your doctor.
How effective is phototherapy for treating psoriasis?
Phototherapy is highly effective for many with psoriasis, reducing symptoms like redness and scaling. However, results vary from person to person.
Are there natural remedies for managing psoriasis symptoms?
While natural remedies like aloe vera and oatmeal baths may provide relief, their effectiveness varies. Consult your doctor before trying alternative treatments.