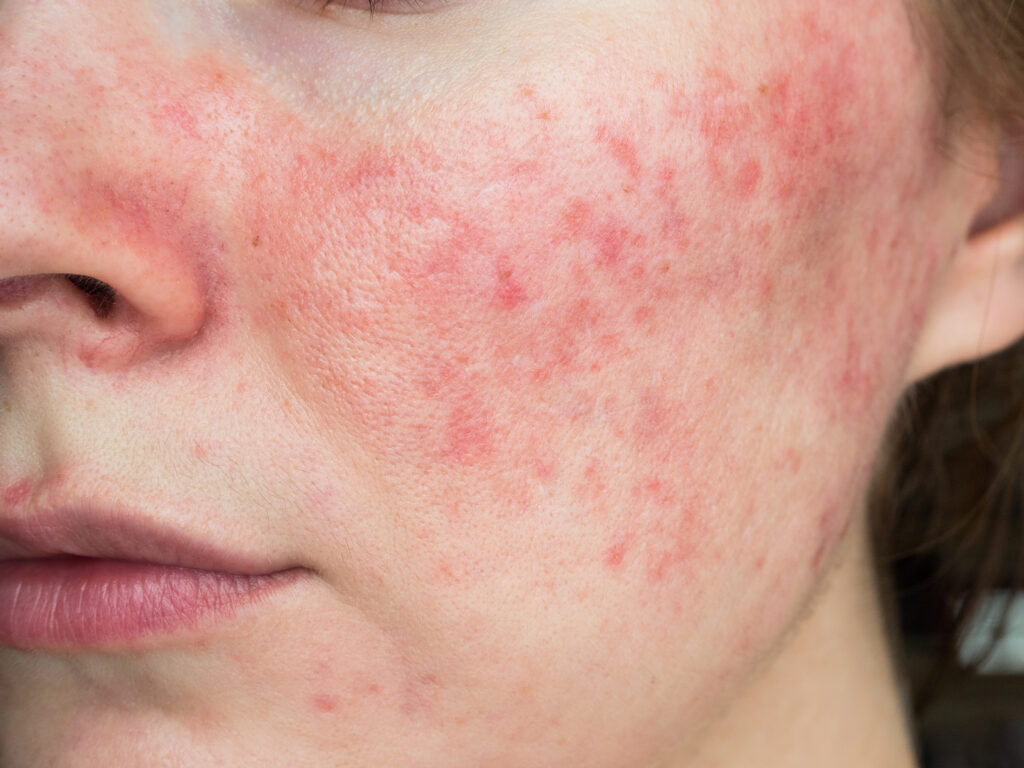
Rosacea is a long-term skin condition, which mainly affects the face, causing redness, swelling, and sometimes acne-like breakouts. It typically starts after 30 but can occur earlier.
While people with fair-skinned are more prone, it can affect anyone. Flare-ups can be triggered by various factors like sun exposure and stress, making management crucial.
Unfortunately, rosacea cannot be cured, but the following treatments can help you to reduce and control symptoms.
How to treat rosacea
When it comes to managing rosacea, finding the right treatment is essential for improving your skin’s health and reducing symptoms.
Alongside prescription creams, antibiotics and topical gels are also commonly used to manage rosacea.
Prescription creams and gels
Prescription creams and gels can help you manage rosacea symptoms effectively. They often contain active ingredients like azelaic acid, metronidazole, and ivermectin, which target inflammation and abnormal blood vessel function.
To use them, follow your GP’s instructions carefully, applying the medication once or twice daily to clean, dry skin. It may take some time to see improvement, and you might experience mild side effects like skin irritation, which usually fade with time.
While these treatments work well for many, they may not be suitable for everyone. If your symptoms persist or worsen, your GP may refer you to a dermatologist for further guidance.
Antibiotics
Antibiotics for rosacea often come in oral and topical forms, which help to target bacteria on the skin’s surface, and reduce redness and swelling.
Oral antibiotics like doxycycline and tetracycline are prescribed for their anti-inflammatory properties. They’re usually taken for several weeks or months, gradually improving symptoms over time.
Topical antibiotics, such as metronidazole and erythromycin, are applied directly to the affected skin to tackle bacteria and inflammation. They’re often used for milder cases or after oral antibiotics.
Frequently asked questions about treating rosacea
What are the most effective prescription creams for rosacea?
The most effective prescription creams for rosacea often contain azelaic acid, metronidazole, or ivermectin. They target redness and inflammation.
How do antibiotics help manage rosacea symptoms?
Antibiotics help manage rosacea symptoms by targeting bacteria on the skin’s surface and reducing inflammation, redness, and the frequency of flare-ups.
What are the common side effects of rosacea treatments?
Common side effects of rosacea treatments may include skin irritation, dryness, burning sensation, and temporary worsening of symptoms.